Analyse database connections
Learn about the best practices to analyze database connections.
Configuration practices
Maximum open database connections to configure
The number of database connections that should be configured depends on the following:
number of concurrent users (not every user opens a database connection)
number of active threads ( the type of how and which censhare modules are configured)
number of remote servers connected (only those that are tunneling the database connection through RMI)
number of configured invocations in DataObjectService
In general, you can calculate a number of 50 maximum open database connections per application server.
Example: Everyone of 4 node application servers should have a value of 50 maximum open database connections configured.
Now, if a remote server doesn't have a direct JDBC database connection and requests it indirectly over RMI from another (mostly the master) server, then the master server needs +50 open database connections, i.e. whose value increases to a maximum of 100 open database connections.
With this info, you can determine the values for your environment by a rule of thumb.
Note that the value is only a soft limit. The real limit of database connections is set by the Oracle parameter processes, respectively its RAM (sga size) allocation.
The value of the processes parameter in Oracle should be set to the result of the following formula:
"processes parameter" > ( "censhare max open JDBC connections" * "number of censhare servers") + "number of oracle background processes"
Example
4 censhare servers: 300 > ( 50 * 4 ) + 50
When to increase the value of maximum open database connections
Increase the value, if you notice the following messages in the ~/work/logs/server-0.0.log even if the DatabaseServiceWatchdog is appearing every 5 minutes within the server log file:
WARNING: S001: DatabaseService: EventServiceWatchdog: maximum number of connections in use,
blocked further access
INFO : T013: HotfolderCheckinNew.processEvents: Service: uk-mal-lin-orac-01.20080915.140146.094[system]: waiting for service:
DatabaseService[uk-mal-lin-orac-01:DatabaseService] database, since: 30000ms
ServiceException[srv-ex-unavailable]: Service 'DatabaseService[uk-mal-lin-orac-01:DatabaseService]'
is not available
SEVERE : DatabaseServiceWatchdog: DatabaseService: DatabaseServiceWatchdog: corpus:
limit of maxOpen connections [100] has been reached, could not open new connectionWhere to configure the open connections and what to consider
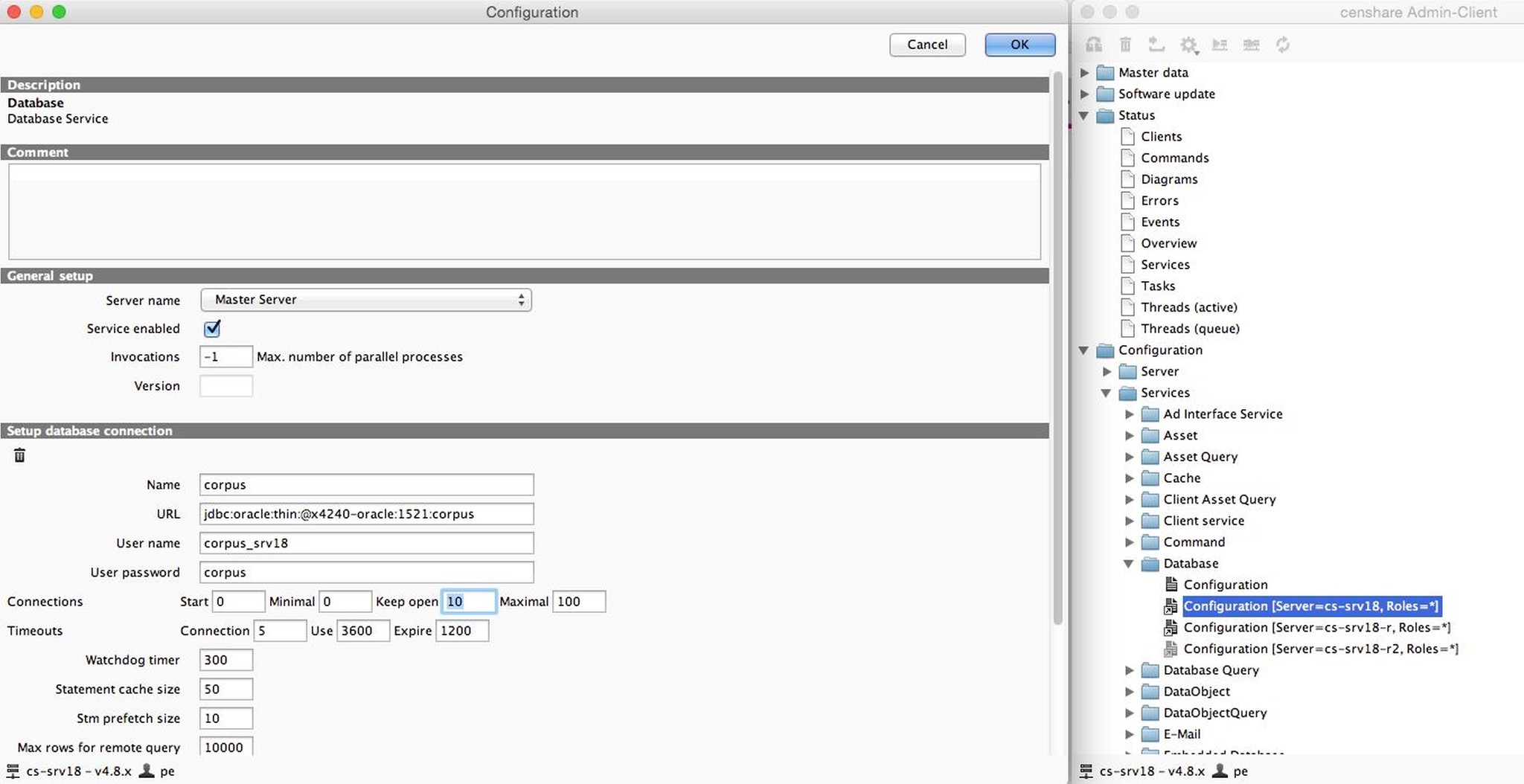
Configure the max-open parameter in one of the following ways:
- in the censhare Admin Client under Configuration | Services | Database
- in the file ~/cscs/app/services/database/config.<server>.xml
Normally, a (remote) configuration refresh is sufficient. Sometimes (e.g. if all database connections are currently exhausted) this requires an application server (JVM) restart.
Performance optimization
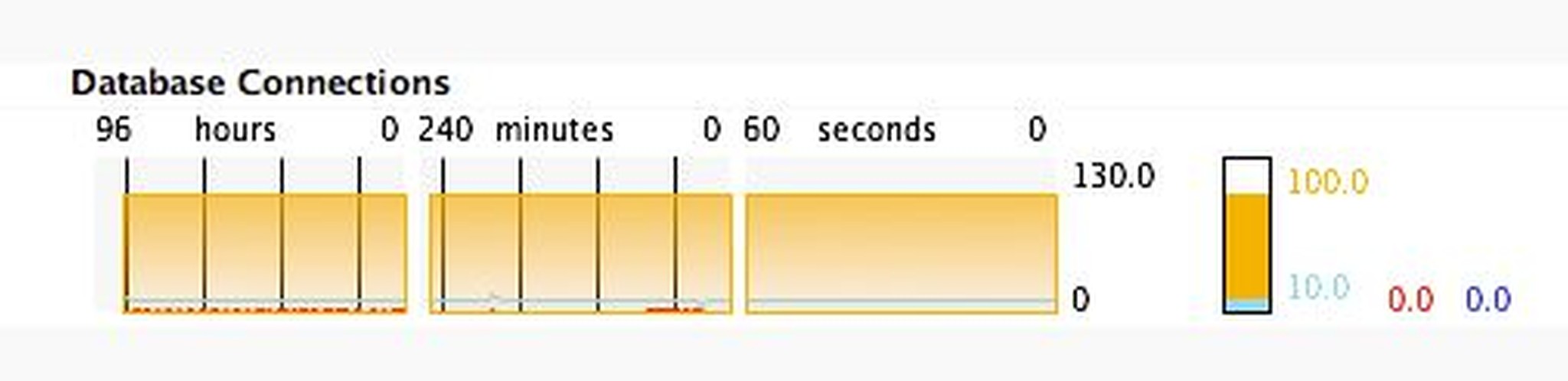
Set the keep-open parameter to the average used database connections. Check the value via the Diagrams / Database Connections.
From a resource perspective, it's cheaper and faster (in the area of milliseconds) to keep a database connection open, compared to opening a new database connection each time.
Troubleshooting
DatabaseServiceWatchdog doesn't appear in the log file
Sometimes, the DatabaseServiceWatchdog is blocked by a thread or while trying to close a physical database connection. As a result, unused database connections are not released and the pool of maximum open database connections gets exhausted. With the following command you can check if the DatabaseServiceWatchog is appearing every 5 minutes:
grep "DatabaseServiceWatchdog:.*checking connections" ~/work/logs/server-0.0.logIf it doesn't appear, this means that it is blocked. For further analysis, you need to create a jstack output of the application server java process. Keep in mind that an older (lower than ~/css/app/common/lib/ojdbc6-v11.2.0.2.4.jar) version of the JDBC driver could lead to blocked physical connection, too.
The following example jstack output shows a BLOCKED DatabaseServiceWatchdog. It describes only one of many possible causes to show the analysis method.
"DatabaseServiceWatchdog" prio=3 tid=0x000000001a67d000 nid=0xa823 waiting for monitor entry [0xffff80ff7bd0d000]
java.lang.Thread.State: BLOCKED (on object monitor) at
oracle.jdbc.driver.PhysicalConnection.closeLogicalConnection(PhysicalConnection.java:4010)
- waiting to lock <0x000000046623c4c8> (a oracle.jdbc.driver.T4CConnection) at oracle.jdbc.driver.LogicalConnection.closeInternal(LogicalConnection.java:258) at oracle.jdbc.pool.OraclePooledConnection.getConnection(OraclePooledConnection.java:306)
- locked <0x000000046623c408> (a oracle.jdbc.pool.OraclePooledConnection) at com.censhare.manager.databasemanager.DatabaseServiceImpl$DBCachedConnection.closePhysical(DatabaseServiceImpl.java:294) ...To find out which thread blocks the DatabaseServiceWatchdog, take the id 0x000000046623c4c8 offline - waiting to lock <0x000000046623c4c8> (an oracle.jdbc.driver.T4CConnection) and search for it within the stack output.
You find out that it's blocked by thread T004 . This thread corresponds to checkConstraints(WConnectionImpl.java:210).
"T004" prio=3 tid=0x00000000028e7000 nid=0x1c runnable [0xffff80ffb74dc000] java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE ... at oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleStatement.executeQuery(OracleStatement.java:1477)
- locked <0x000000046623c4c8> (an oracle.jdbc.driver.T4CConnection) at oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleStatementWrapper.executeQuery(OracleStatementWrapper.java:392)
at com.censhare.server.support.wsql.WConnectionImpl.checkConstraints(WConnectionImpl.java:210)
at com.censhare.server.support.wsql.WConnectionImpl.prepareStep(WConnectionImpl.java:428)
at com.censhare.manager.dataobject.DataObjectServiceImpl.executeUpdate(DataObjectServiceImpl.java:114) ...It means that within the DatabaseService configuration the parameter is set to constraint-check-enabled="true".
Find out which thread uses a database connection
Since censhare Server version 5, there's an option within the XML of the database service called track-allocations="false". If you set it to true and refresh the database service, you can see the transaction ID of the thread which uses a database connection. With a grep for the transaction ID you can find out the censhare command/module which holds the database connection.
Example
grep "DatabaseServiceWatchdog:.*was last accessed by" ~/work/logs/server-0.0.log ... 2015.03.13-11:48:40.971
INFO : DatabaseServiceWatchdog: DatabaseService: DatabaseServiceWatchdog:
used connection[116] was last accessed by server.20150313.113841.018: 2015-03-13T10:48:16.894Z ...
grep server.20150313.113841.018 ~/work/logs/server-0.0.log ... 2015.03.13-11:49:16.898 INFO : T061: CommandExecutor: server.20150313.113841.018[system]:
content_export2.aa-content-export2-20140716-1114-0 error in 90006ms ...grep "DatabaseServiceWatchdog:.*was last accessed by" ~/work/logs/server-0.0.log 2017.07.12-12:34:19.751 INFO : DatabaseServiceWatchdog: DatabaseService: DatabaseServiceWatchdog:
used connection[203] was last accessed by server.20150313.113841.018[export-combine.pdf][censhare]: 2017-07-12T10:34:15.394Z