Search & filter assets
censhare offers different types of searches: Quick Search, Detailed Search, and Expert Search. You can combine some search types to benefit from their advantages.
Overview
censhare has three different types of searches:
Quick search: With the Quick search, you enter your terms in the search field in the Top Navigation. Auto-suggestion filters display while you are typing. You can select a filter. A search entry is then only applied to the selected asset property. For performance reasons, the Quick search interprets a subset of all asset properties. Your search results are a subset of all possible results for your entered text.
Detailed search: The Detailed search allows you to search for a specific asset property or combination of asset properties. You only get a result if there is a match for the selected asset property or combination. The Detailed searches offer a larger subset with commonly-needed asset properties to search within than the Quick search.
Expert search: With the Expert search, you can search for any asset property and relation that is available in censhare. You can create searches that include different asset properties and content within an asset structure. This requires a deeper knowledge of censhare and especially the search functionality.
Search combinations
Each of the three search functions has advantages and drawbacks. You can combine the different search functions to suit your needs:
Quick search and Detailed search
Quick search and Expert search
For example, you can search for assets with the Text asset type that have been edited within the last two days. Use the Quick search for the Text asset type. Define the time frame within the Detailed search. censhare then combines the results of the two search definitions.
By default, censhare combines the Detailed/Expert search and the Quick search parameters with an AND operator. If desired, you can change this to an OR operator. In this case, censhare shows every asset that results from the Detailed/Expert search or the Quick search parameters.
You can also convert an existing Detailed search into an Expert search. For example, you searched for the "Text" asset type in the Detailed search. Now, you want to see only the Text assets that have an Author assigned. This is not possible in the Detailed search. Instead of creating a new Expert search, you can convert the Detailed search into an Expert search and add the condition for a child relation with the Assignment/Author type.
How the searches work
The Quick Search
censhare calculates a result set for each filter tag and text entry. The result sets are combined and the intersection of all the result sets is shown as the result.
Quick search: In a Quick search, the result sets of the search entries are combined. The intersection of the result sets is the result of the search (5). In this example, the Quick search field (3) contains a filter tag (1) with a result set (6) and a text entry (2) with a result set (4). By default, the result sets are combined with an AND operator.
When you select an auto suggestion for your search text, censhare shows the selected text as a filter tag in the Quick search field.
The Detailed search and the Expert search
When you enter a Detailed search or an Expert search, the search is represented by a tag in the Quick search. The result of the Detailed/Expert search is shown as the search result.

Expert/Detailed search: In an Expert or Detailed search the result set (3) is shown as a tag (1) in the Quick search field (2).
You can either use a Detailed search or an Expert search, you cannot use both at the same time.
Detailed or Expert search combined with the Quick search
You can combine a Detailed or Expert search with search entries for the Quick search. censhare calculates the result set of the Detailed/Expert search first. This result set is combined with the result sets of the Quick search entries. The search result is the intersection of the result sets.

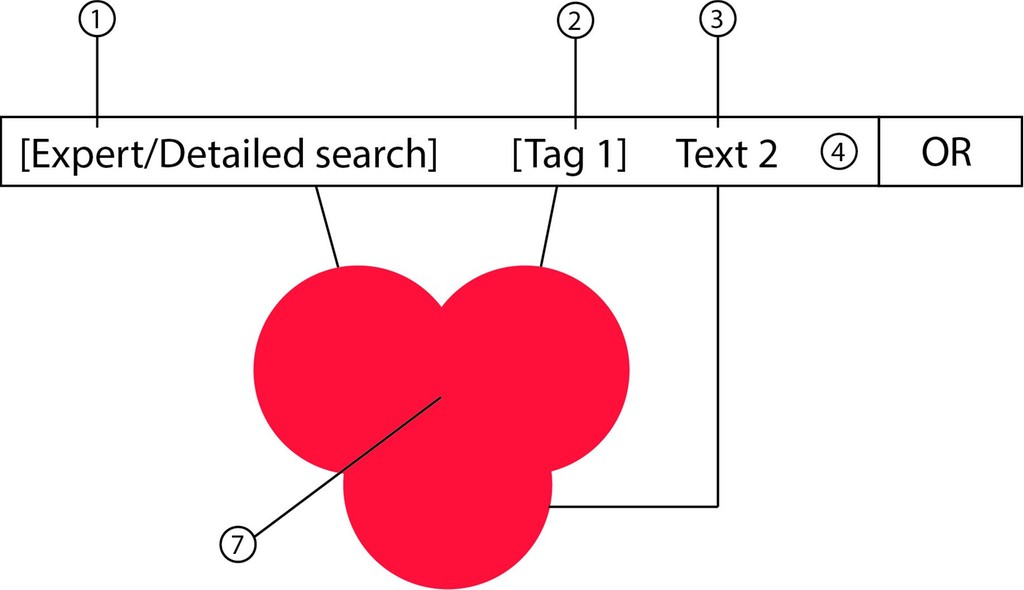
Combination search: The result set (7) is the intersection of the result set (8) of the Expert/Detailed search (1) and result sets (5) and (6) of the entries for the Quick search in the Quick search field (4). In this example, the Quick search contains a filter tag (2) and a text entry (3).
If you convert the Detailed search into an Expert search and edit it, your changes only affect the result set of the Detailed/Expert search, the result sets of the Quick search entries remain unchanged. The search result is the intersection of all result sets.
The OR operator
You can use the OR operator instead of the AND operator to combine the result sets of the Detailed/Expert search with the entries of the Quick search. The operator does not change the result set of the Detailed/Expert search.

OR operator: If you choose the OR operator, the result set consists of all results from the Expert/Detailed search (1) and entries of the Quick search. In this example, the Quick search entries are the filter tag (2) and a text entry (3).
When to use which type of search?
Quick search
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Detailed search
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Expert search
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Content
Related articles
Error rendering macro 'contentbylabel'
Invalid label: " user"