The dataflow between an HCMS instance and a target application can be secured against failures in various ways; by design, it is secured through using multiple delivery servers, called satellites, bundled into groups, like on the diagram below:
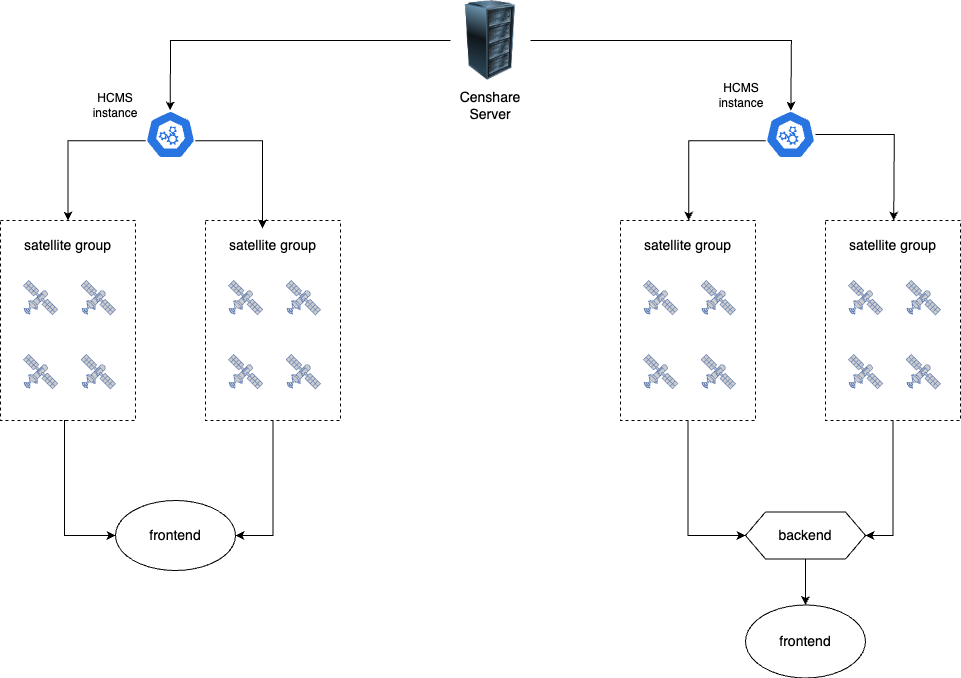
The number of satellite groups and satellites in the group can be as big as your project requires.
Satellite group and its purpose
A satellite group (cluster) is a group of satellites without unique ids, bundled together. On the Censhare Server, they share the same asset as well as the same certificate. To distinguish between them, a random suffix is generated on start and changes with each new start respectively.
A satellite cluster is designed for scalability and robustness: if one satellite in the group/cluster fails, the others continue to serve data. A satellite group will be created by default, even if you have only one satellite in it. However, it is highly recommended to run more than one satellite in each group.
How many satellites and/or satellite groups are optimal
Any production setup should have at least two satellites running. This ensures a fault tolerance. You should also make sure all satellites do not run on the same hardware, e.g., their VMs should be separated too. A good setup would have everything running twice on two physical machines.
How many of the satellites you actually need, depends mostly on the amount of traffic you expect and your cost constraints. The rule of thumb is the following:
If the CPU load (of one satellite) rises above 50%, consider adding another satellite. At 75%, it is definitely required.
You can add and remove satellites to the group at any time without any changes in the configuration. An orchestration platform like Kubernetes or AWS ECS will do it for you automatically.
Adding multiple satellite groups is helpful for serving data to different geographic regions. In such a setup, each geographic location should be covered by its own satellite group.
How to create and manage
When you register a new HCMS instance using the CLI tool, the configuration create command will implicitly create one configuration (group) as well as one satellite group, with basic essential configuration.
Updating configuration and satellite groups is possible using either the CLI tool, or the Admin Client, or by accessing the XML assets directly.
Adding or removing satellites means starting or stopping Docker containers on the same or different servers/VMs. Exact steps depend on your setup:
-
For Docker-based but self-hosted installation you just need to run the Docker container (from the same image) on as many servers/VMs as the amount of satellites you want to use.
-
The same for any other self-hosting.
-
For AWS-based and manually managed hosting, you need to add new tasks to your ECS instance, one task represents one satellite.
-
AWS ECS, Kubernetes and other orchestration platforms also can spin up and shut down satellites automatically, based on the current load and other parameters.
It is possible to deploy standalone single satellites without a satellite group, but this is not recommended.
It is also possible to move satellite groups between configuration groups, but it needs to be done manually, using the CLI tool or the Admin Client. Such movements are only necessary for any kind of self-hosting.